In recent times there has been an increase in the number of bed bugs infestations in Auckland and throughout New Zealand.
A contributing factor to this increase is world travel, with bed bugs being spread in luggage, shoes and clothing. Once present at high turnover accommodation, the hitchhiking bugs may then be transported and brought back to the homes of guests in their luggage. This can allow for a new infestation to occur inside the home.
WHAT ARE BED BUGS?
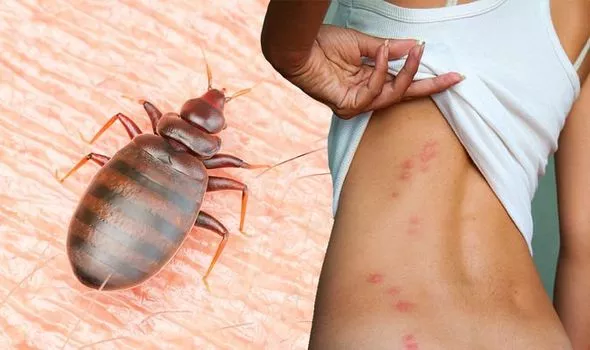
Bed bugs are small oval-shaped and flat insects which can grow up to 5mm long, changing colour from cream to brown as they mature. Adults have flat bodies about the size of an apple seed. Bed bugs need to feed on blood to grow, are extremely resilient and can live for up to one year without a feed.
They tend to live in cracks and crevices in and around your bed, especially in mattress seams and travel on clothing, furniture, bedding and luggage. Their preference is to feed on humans but will also feed on other warm-blooded animals. Feedng time is generally at night.
While they do not transmit diseases, these little pests are upsetting and can very difficult to eliminate.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS OF AN INFESTATION?
You may have bed bugs if you notice the following:
- regularly waking with bites
- bugs on your mattress, bed frame and other furniture
- dark or rusty spots of bedbug excrement on sheets and mattresses, bed clothes, and walls.
- blood stains on your sheets or pillowcases
- an offensive musty, sweet smell from the bugs’ scent glands
Bites can cause red, itchy spots that are often found on legs, arms and shoulders. Some bites can become infected. Some people do not react, while others may not react until up to 9 days after they are bitten.
HOW TO GET RID OF BED BUGS?
This pest is particularly problematic to treat, with complete eradication unlikely to be achieved with a single treatment. Pesticides may kill the bugs but they are largely ineffective on the eggs. Follow up inspections are nearly always required and further treatments are often necessary.
The survival of eggs is also an issue. It is not uncommon for the live bugs amongst an infestation to be completely eradicated during an effective treatment cycle, only to have the remaining or surviving eggs hatch and populate the location once again. The eggs can also have an incubation period of up to two weeks and may be deposited in hidden areas that are difficult to treat.
Once an infestation is detected, all adjoining rooms should to be inspected and treated if also affected.
INFESTATION PREVENTION
You can help prevent infestations by:
- avoiding using second-hand mattresses
- regularly checking your bed for bed bugs
- maintain an appropriate cleaning regime such as regular vacuuming behind beds.

Recent Comments